Infertility affects millions of couples worldwide, making assisted reproductive technologies essential for achieving pregnancy. One such advanced technique is Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI), a specialized form of In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) that enhances fertilization success. But who exactly needs this procedure
Let’s explore the key candidates for ICSI and how it can help overcome fertility challenges.
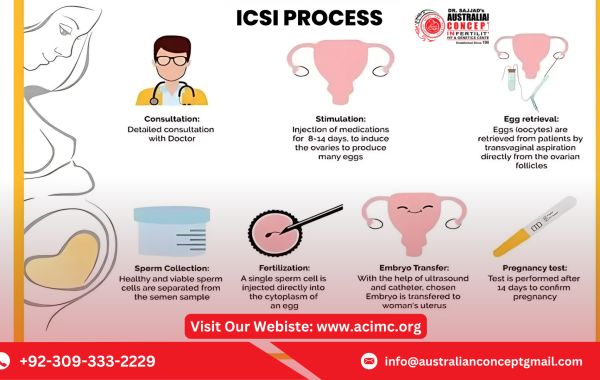
What Is the ICSI Procedure?
ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) is a laboratory-based procedure where a single, healthy sperm is directly injected into a mature egg to facilitate fertilization. This method is particularly beneficial for couples facing severe male infertility or previous failed fertilization attempts through conventional IVF.
Unlike traditional IVF, where sperm must naturally penetrate the egg, ICSI ensures fertilization by bypassing the natural barriers, making it a highly effective solution for various fertility issues.
Who Needs the ICSI Procedure?
ICSI is recommended in several situations, particularly when natural conception or standard IVF methods have failed. The following are the most common cases where ICSI is needed:
1. Male Factor Infertility
One of the primary reasons for choosing ICSI is male infertility, which can result from:
- Low sperm count (Oligospermia): When the sperm count is significantly below normal, making natural fertilization difficult.
- Poor sperm motility (Asthenospermia): Sperm cannot swim effectively to reach and fertilize the egg.
- Abnormal sperm shape (Teratospermia): When a high percentage of sperm have irregular shapes, reducing their ability to penetrate the egg.
For men with any of these sperm-related issues, ICSI offers a direct method to achieve fertilization.
2. Azoospermia (No Sperm in Ejaculate)
Azoospermia is a condition where a man’s semen contains no sperm. This can be due to:
- Obstructive azoospermia: A blockage in the reproductive tract prevents sperm from reaching the ejaculate. This can be caused by prior vasectomy, infections, or congenital conditions.
- Non-obstructive azoospermia: The testicles do not produce enough sperm due to genetic disorders, hormonal imbalances, or other medical conditions.
ICSI can be performed using surgically retrieved sperm from the testicles through procedures like TESA (Testicular Sperm Aspiration) or PESA (Percutaneous Epididymal Sperm Aspiration).
3. Failed Fertilization in Previous IVF Cycles
Some couples undergo traditional IVF but fail to achieve fertilization due to unknown reasons. If previous IVF cycles did not result in fertilized embryos despite normal sperm count and motility, ICSI can be a solution to increase fertilization success.
4. Use of Frozen Sperm Samples
In cases where sperm is collected and frozen for later use (such as before chemotherapy or testicular surgery), thawed sperm may have reduced motility, making natural fertilization difficult. ICSI helps by injecting a single healthy sperm directly into the egg, increasing the chances of successful fertilization.
5. Use of Donor Sperm or Egg Freezing
Couples using donor sperm due to male infertility or frozen eggs (which have harder outer shells) often benefit from ICSI. The direct injection method ensures the sperm successfully penetrates the egg.
6. Genetic Disorders and Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Men with genetic disorders that can be passed to their offspring (e.g., Klinefelter Syndrome, Y-chromosome microdeletions) may require ICSI, often combined with Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT), to ensure only healthy embryos are implanted.
7. Unexplained Infertility
Some couples face infertility with no identifiable cause. If natural conception and standard IVF have not worked, ICSI provides an alternative approach to increase fertilization rates.
Success Rates of ICSI
ICSI is highly effective, with a fertilization success rate of 70–80% per egg injected. However, overall pregnancy success depends on several factors, including:
- Age and egg quality of the female partner
- Sperm health and genetic factors
- Expertise of the fertility clinic
While ICSI improves fertilization rates, embryo quality and implantation success are still dependent on overall reproductive health.
Are There Any Risks with ICSI?
Although ICSI is a safe and widely used procedure, there are some potential risks, including:
- Egg Damage: A small percentage of eggs may be damaged during sperm injection.
- Increased Risk of Genetic Disorders: If the underlying male infertility is genetic, the child may inherit similar conditions.
- Higher Risk of Multiple Pregnancies: If multiple embryos are transferred, there is a chance of twins or triplets, leading to pregnancy complications.
To minimize risks, couples are advised to consult with an infertility specialist and consider genetic counseling if necessary.
Conclusion
The ICSI procedure is a revolutionary treatment for couples struggling with severe male infertility, azoospermia, repeated IVF failures, and genetic conditions. It offers higher fertilization success rates and makes parenthood possible even in the most challenging infertility cases.
If you are experiencing fertility issues and wondering whether ICSI is right for you, consult a trusted infertility specialist to explore the best treatment options tailored to your needs.