Telematics 2.0 is introducing a more advanced layer of capability, where artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are being integrated to enable dynamic pricing, predictive maintenance, and proactive risk management. This shift moves the conversation from merely tracking driving behaviors to gaining deeper insights and building a strategic advantage in the insurance landscape.
From Simple Data Collection to Contextual Intelligence
The first generation of telematics car insurance was focused on basic data like mileage, speed, and braking patterns. However, Telematics 2.0 is evolving toward a more sophisticated, context-aware approach. Insurers are not only interested in the “how” of driving but also the “where,” “when,” and “under what conditions.”
The goal is not just to gather data for the sake of it, but to make that data work smarter. Telematics 2.0 integrates contextual intelligence—such as weather conditions, traffic patterns, and road hazards—directly into risk models, helping insurers create more accurate and dynamic pricing structures. This integration allows insurers to offer policies that can adjust in real time based on environmental and situational factors, improving risk assessments and underwriting practices.
Telematics and Predictive Maintenance: Unlocking New Revenue Streams
While predictive maintenance has long been a staple of fleet management, it is now gaining traction in the broader insurance market. By using telematics, insurers can shift from being passive risk managers to active safety partners.
Munich Re has demonstrated how insurers can use vehicle diagnostics to offer predictive maintenance services, preventing breakdowns before they occur and reducing claims. They provide a telematics product that can be easily integrated into existing insurance platforms via a white-label app or a customizable SDK. This integration offers insurers advanced risk-scoring capabilities and access to cutting-edge technology, enhancing their service offerings.
By combining telematics with IoT and AI, insurers can now enhance their predictive maintenance capabilities even further. For example, usage-based insurance models are being refined with machine learning algorithms that predict potential vehicle failures, enabling insurers to recommend maintenance proactively. Companies like State Farm are already using AI-driven telematics to provide real-time suggestions to drivers, improving vehicle health and safety. Such innovations have led to up to a 30% improvement in risk assessments and a 20% reduction in accident rates.
Behavioral Science and Gamification: Engaging Drivers Beyond Discounts
While usage-based insurance (UBI) has been well-established, Telematics 2.0 is taking things a step further by incorporating behavioral science principles and gamification into the mix. Rather than simply offering discounts for good driving, insurers are now using techniques like scoring, leaderboards, and rewards to influence driving behavior actively. This approach not only lowers claims but also fosters stronger customer engagement and loyalty.
Research from the University of Guelph shows that adding gamification to telematics programs can increase participation, particularly among younger drivers, by making the experience more interactive and rewarding. Companies like Root Insurance have taken this concept further by using telematics-driven gamification to offer personalized pricing, with safe drivers receiving significant discounts. Their approach has resulted in a 15% reduction in claims compared to traditional models.
Cambridge Mobile telematics car insurance reports that incorporating behavioral feedback and gamification into telematics programs can reduce accident risks by up to 40%, showcasing the power of these innovative approaches in improving driver behavior and overall safety.
Telematics in Broader Ecosystem Partnerships
An exciting but underexplored opportunity lies in using telematics data as a shared asset across broader ecosystems. Insurers can form strategic partnerships with car manufacturers, city planners, and even retailers. For instance, telematics data could be used to inform the development of smarter urban infrastructure, leading to safer roads and more efficient traffic management.
An example of this is Audi’s Traffic Light Information system, which integrates vehicle data to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion. Similarly, telematics partnerships with retailers can offer customers discounts based on their driving habits, integrating insurance more seamlessly into daily life. Progressive’s Snapshot program, for example, uses telematics data to offer targeted discounts, enhancing customer engagement and providing valuable insights into driving behaviors.
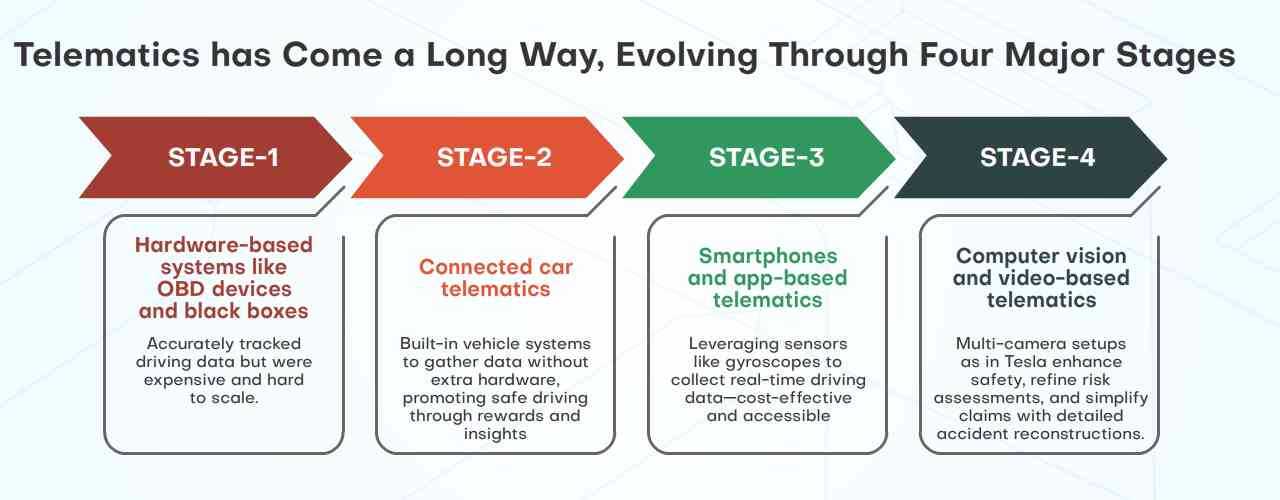
Leveraging AI and Machine Learning to Manage Data
With the vast amounts of data generated by telematics devices, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are becoming indispensable tools for insurers. AI can uncover patterns in driving behavior that might not be immediately obvious to human underwriters, enabling real-time risk assessment and fraud detection. This capability not only speeds up claims processing but also helps insurers proactively mitigate risks by anticipating high-risk behaviors before they result in accidents.
Emerging Trends in Telematics
The future of telematics car insurance is poised for exciting developments:
Connected Vehicles and 5G: The rise of connected vehicles, combined with the power of 5G technology, will allow insurers to make instantaneous policy adjustments and provide more accurate risk assessments in real time.
Embedded Insurance Models: More insurers are integrating telematics into embedded insurance solutions, offering seamless, personalized insurance options at the point of sale.
Environmental Impact Tracking: In the future, telematics may also track carbon emissions and encourage eco-friendly driving behaviors, aligning insurance offerings with sustainability goals and promoting greener driving habits.
Telematics 2.0 is set to revolutionize the insurance industry by not only improving risk management but also creating more personalized, engaging, and dynamic customer experiences. The possibilities are vast, and insurers are only just beginning to explore this new frontier.








