Creative Diagnostics, a leading manufacturer and supplier of antibodies, antigens and assay kits, has recently announced a series of new Anti-Small Molecule Label Antibodies to facilitate the development of nucleic acid lateral flow immunoassay (NALFIA). These antibodies can specifically bind to small molecule labels and offer customers multiple choices, including Anti Digoxin monoclonal antibodies, Anti-Fluorescien monoclonal antibodies, and Anti-FAM polyclonal antibodies.
Traditional nucleic acid detection methods require trained operators and sophisticated instrumentation, with signal reading and detection times often taking hours. With the increasing demand for diagnostics in resource-limited settings, lateral flow assays (LFAs) for nucleic acid testing are receiving increasing attention due to their low cost and ease of use. They have also shown great potential in point-of-care testing (POCT).
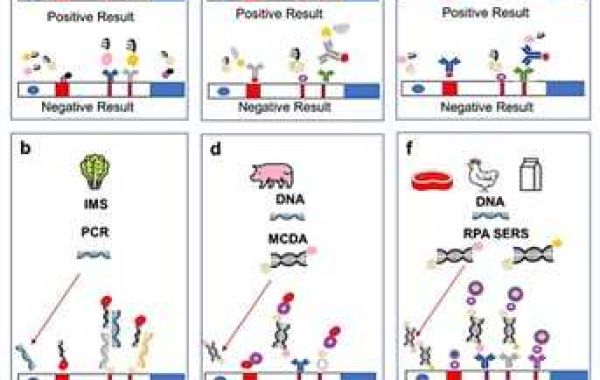
Currently, target gene amplification has been widely used in diagnostic settings. Among them, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and isothermal methods such as loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), multiple cross displacement amplification (MCDA), and recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) have been introduced into the lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) of nucleic acids, termed nucleic acid lateral flow immunoassay (NALFIA). NALFIA combines lateral flow technology with immunoassay principles for the detection of nucleic acid-related products.
A typical workflow for nuclear lateral flow testing includes nucleic acid extraction from biological samples, nucleic acid amplification, and detection of amplicons by LFAs using colorimetric labeling materials. For NALFIA, both forward and reverse primers are typically labeled with biotin and another antigen with high antibody affinity (e.g., digoxin (DIG), carboxyfluorescein (FAM), and/or FITC). In this way, the amplicon is doubly labeled and forms a sandwich-type complex through a high-affinity immunoreaction between the antigen and the antibody. Each monoclonal antibody specifically recognizes the corresponding tag.
For example, the Anti Digoxin monoclonal antibody (Catalog # CABT-L2334) is suitable for use in ELISA. Digoxin is a beta-blocker drug originally derived from the foxglove plant, Digitalis lanata. Digoxin is used primarily to improve the heart’s ability to pump blood in patients with congestive heart failure (CHF) and to treat problems such as high blood pressure. It is also used to help normalize certain heart arrhythmias (abnormal types of heartbeats).
Another is the Anti-Fluorescien monoclonal antibody (Catalog # DMAB7251). FITC (fluorescein isothiocyanate) is a fluorescent dye that absorbs ultraviolet or blue light, causing the molecule to excite and emit visible yellow-green light. This emission stops when the light that caused the excitation is removed. When one of the reactants is part of a cell, tissue, or other biological structure, fluorescent labeling can quickly and accurately localize antigen-antibody interactions. FITC is a commonly used antibody marker in immunofluorescence techniques because it is relatively easy to attach to proteins and generally does not interfere with the biological activity of the labeled proteins. FITC is used to label a wide range of different proteins.
To learn more information about the Anti-Small Molecule Label Antibodies, please visit https://www.creative-diagnostics.com/tools-for-nucleic-acid-lateral-flow-immunoassay-nalfia-anti-small-molecule-label-antibodies.htm.
About Creative Diagnostics
Creative Diagnostics is a leading manufacturer and supplier of antibodies, viral antigens, innovative diagnostic components, and critical assay reagents. In addition to providing contract RD and biologic manufacturing services for diagnostic manufacturers along with GMP biologics manufacturing for the biopharmaceutical market, the company aims to continue to act as a trusted source for all researchers’ assay development and manufacturing needs.