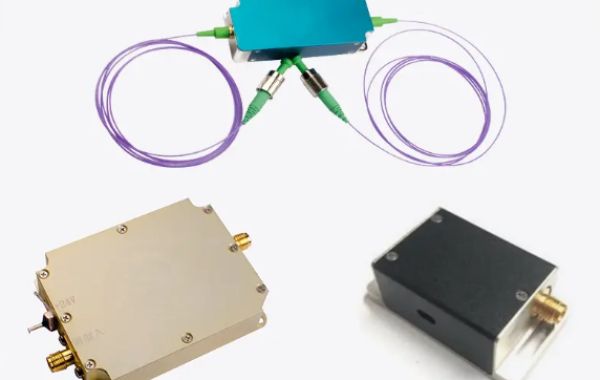
To mitigate these limitations and achieve accurate delay measurements, consider the following tips:
Calibration
- Regularly calibrate the MADL using a calibrated delay source or interferometer.
- This ensures that the device's delay readings are accurate and consistent.
Temperature Control
- Maintain a stable temperature environment to minimize thermal expansion effects on the fiber.
- Temperature fluctuations can introduce unwanted delay variations.
Vibration Isolation
- Isolate the MADL from vibrations to prevent unintended delay fluctuations.
- Vibration can cause mechanical instability and affect the fiber's length.
Proper Handling
- Avoid excessive force or bending of the fiber, which can introduce unintended delays and polarization changes.
- Handle the fiber carefully to minimize stress.
Slow and Steady Adjustments
- Make slow and steady adjustments to the delay mechanism to avoid overshooting the desired delay.
- Rapid adjustments can introduce mechanical vibrations and inaccuracies.
Monitor Polarization State
- Use polarization-maintaining fiber and polarization-sensitive components to preserve the polarization state of the light.
- Monitor the polarization state at the output of the MADL to ensure that it remains stable.
Use High-Quality Components
- Choose a MADL with high-quality components, such as precision-engineered spools and smooth adjustment mechanisms.
- High-quality components can improve the device's accuracy and reliability.
By following these guidelines, you can maximize the accuracy and reliability of your delay measurements with a manual adjustable fiber delay line.