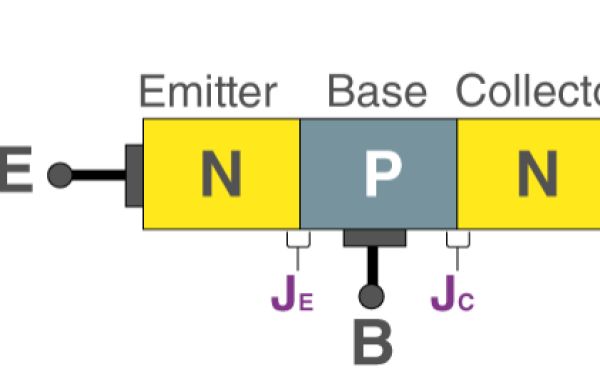
What is a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)?
A three-terminal bipolar junction transistor is a semiconductor component that has two p-n junctions that can amplify or magnify a signal. It is a device that is current-controlled. The base, collector, and emitter are the three terminals on a BJT. A signal of modest amplitude applied to the transistor's base is available at the collector in amplified form. This is the amplification that the BJT offers. Keep in mind that the amplification procedure does require an external source of DC power supply. NPN transistors are frequently utilized in circuits in daily life. The MMBT3904 NPN transistor, for instance, is frequently used in TVs and other home appliances. Hence it is beneficial for us to gain a foundational understanding of BJT.
Bipolar Junction Transistor Symbol
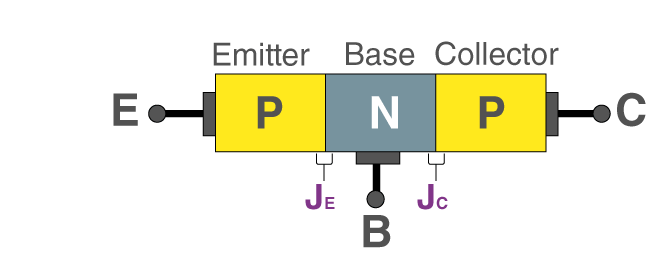
The n-type semiconductor is positioned between the two p-type semiconductors of a PNP BJT. While the n-type semiconductor serves as the base, the two p-type semiconductors function as the emitter and collector, respectively. The illustration below illustrates this.
The current enters the transistor through the emitter such that the emitter-base junction is forward biased and the collector-base junction is reverse biased.
NPN BJT
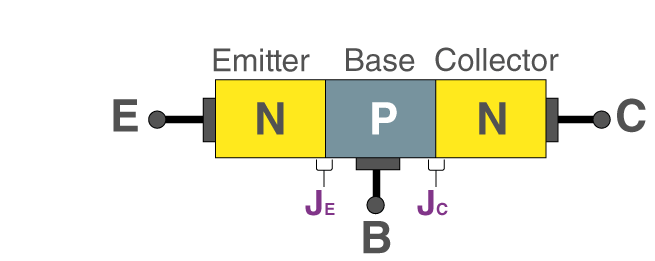
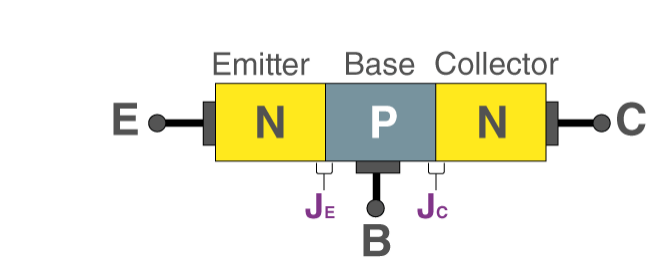
In NPN BJT, p-type semiconductor is sandwiched between the two n-type semiconductors. The two n-type semiconductors act as emitter and collector respectively while the p-type semiconductor acts as a base. This is shown in the figure below.
Current entering the emitter, base, and collector has the sign convention of positive while the current that leaves the transistor has the sign convention of negative.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Who invented BJT?
BJT was invented by W.H Brattin, Bardeen, and William Shockley.
What are the operating regions of BJT?
The operating regions of BJT are:
- Forward active or active region
- Reverse active or inverted region
- Saturation
- Cut-off
What are the applications of BJT?
Following are the applications of Bipolar Junction Transistor:
- It is used as an amplifier
- It is used as an oscillator
- It is used as a demodulator
What happens if the transistor is not biased properly?
Following is the list of consequences if the transistor is not biased properly:
- The work efficiency of the transistor reduces
- There will be a distortion in the output signal
- The operating point may shift
- Transistor parameters will change
Why is there a maximum limit for the collector supply voltage for a transistor?
There is a maximum limit for the collector supply voltage for a transistor because when the collector current is increased rapidly there are chances of the transistor getting damaged. To avoid this, the voltage in the collector should have a maximum limit.
You may also like: The Best Guide to Transistor